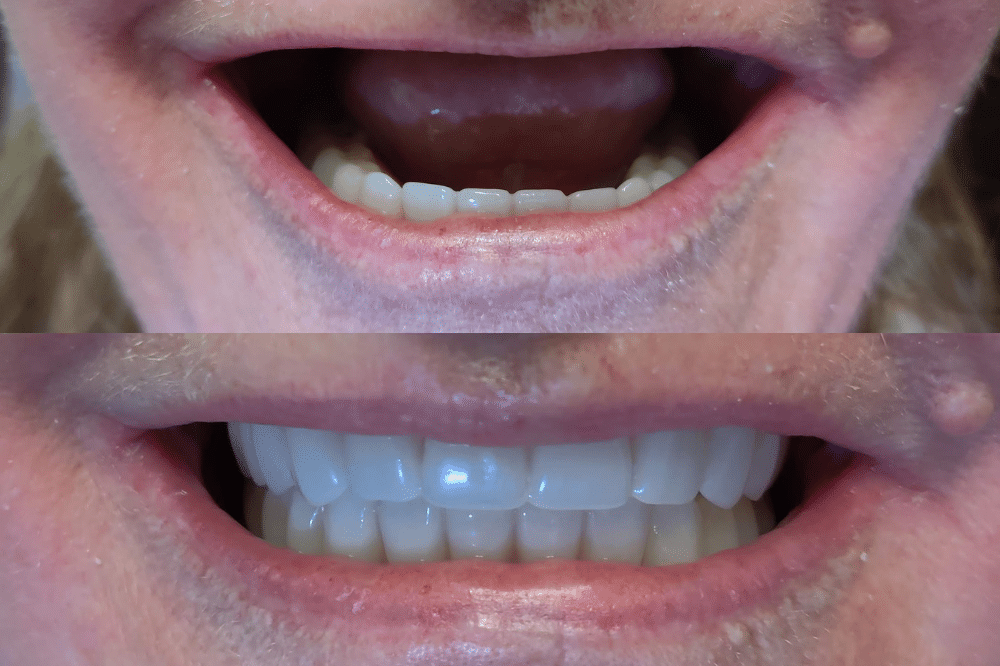
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common condition that affects the gums, bone, and surrounding tissues of the teeth. It can range from mild gingivitis, which is easily treatable, to severe periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss. There are several factors that can contribute to the development of gum disease. In this blog post, we will discuss the major causes of gum disease.
Plaque Buildup
Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the gums and teeth. If it is not removed through brushing and flossing, it can harden into tartar and lead to gum disease. Plaque buildup can cause inflammation of the gums, which can lead to redness, swelling, and bleeding. Regular dental checkups and cleanings can help prevent plaque buildup and keep your gums healthy.
Smoking & Chewing Tobacco
Smoking and chewing tobacco can also contribute to gum disease. Tobacco use can reduce blood flow to the gums, making it harder for them to heal. It can also make it easier for bacteria to stick to the teeth and gums, leading to inflammation and infection. If you smoke or chew tobacco, quitting can help improve your oral health and reduce your risk of gum disease.
Hormonal Shifts During Pregnancy
Hormonal shifts during pregnancy can also increase the risk of gum disease. Pregnancy gingivitis is a type of gum disease that affects many pregnant women. It is caused by the hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, which can make the gums more sensitive to plaque and bacteria. Pregnant women should practice good oral hygiene and see their dentist regularly to prevent and treat gum disease.

Prescription Medications
Certain prescription medications can also contribute to gum disease. Medications that reduce saliva production, such as antihistamines and antidepressants, can make it harder for the mouth to naturally clean itself. This can lead to dry mouth, which can increase the risk of gum disease. If you are taking prescription medications, talk to your dentist about any potential side effects on your oral health.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies can also contribute to gum disease. A diet that is low in nutrients, particularly vitamin C, can weaken the immune system and make it more difficult for the body to fight off infections. This can increase the risk of gum disease and other oral health problems. Eating a balanced diet that is rich in fruits and veggies can help keep your gums healthy.
Crooked Teeth
Crooked or misaligned teeth can also contribute to gum disease. Teeth that are too crowded or too widely spaced can make it harder to clean between them, which can lead to plaque buildup and gum disease. Orthodontic treatment—such as braces or clear aligners—can help straighten teeth and improve oral hygiene.
Family History
Finally, genetics can also play a big role in the development of gum disease. If you have a family history of gum disease, you may be more likely to develop the condition yourself. Regular dental checkups and cleanings can help detect and treat gum disease early, before it becomes more serious.
There are several factors that can contribute to the development of gum disease, including plaque buildup, smoking and chewing tobacco, hormonal shifts during pregnancy, prescription medications, nutritional deficiencies, crooked teeth, and family history. By practicing good oral hygiene and seeing your dentist regularly, you can help prevent and treat gum disease and keep your gums healthy. Do you need a dental check-up? Dental Arts San Diego is here to help! Schedule an appointment by calling (619) 444-1001 or clicking here. We are located at 707 Arnele Avenue, El Cajon, CA, 92020.