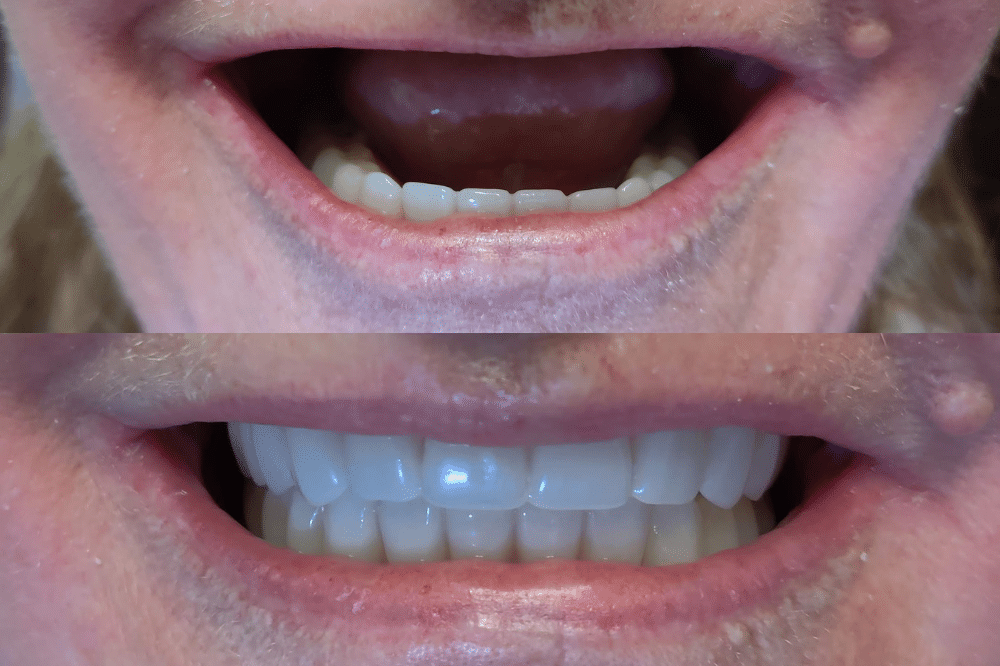
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection of the gums and tissues that support the teeth. It is caused by a buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth, which can lead to inflammation and damage to the gums and bone surrounding the teeth.
The early stage of gum disease is called gingivitis, which is characterized by red, swollen, and bleeding gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which involves more severe inflammation and damage to the gums and bone, leading to tooth loss.
Risk factors for gum disease include poor oral hygiene, smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and certain medical conditions such as diabetes and immune disorders.
Treatment for gum disease may include professional cleaning, scaling, root planing, pocket reduction surgery, bone grafting, guided tissue regeneration, or dental implants. Proper oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, is also crucial for preventing and treating gum disease. Gum disease treatments include the following non-surgical and surgical procedures:
NON-SURGICAL PROCEDURES
Scaling and Root Planing
Scaling and root planing is a non-surgical periodontal therapy that is commonly used to treat gum disease, also known as periodontitis. Gum disease is a bacterial infection of the gums and supporting structures of the teeth, and if left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss.
Scaling and root planing is a deep cleaning procedure that involves removing plaque and tartar from the surface of the teeth and the roots of the teeth below the gum line. This procedure is usually performed by a dentist or dental hygienist and may require multiple visits to complete.
During scaling, the dentist or hygienist will use specialized tools to remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and roots. Root planing involves smoothing the surface of the roots to remove any rough spots that can attract bacteria and cause further infection. The procedure may also involve the use of local anesthesia to make the patient more comfortable during the cleaning process.
After the procedure, the dentist or hygienist may prescribe antibiotics to control any remaining infection, and the patient will be advised on proper oral hygiene techniques and maintenance procedures to prevent future infections.
Scaling and root planing are effective treatments for gum disease, but it is important to follow the recommended oral hygiene practices and maintain regular dental check-ups to prevent the recurrence of gum disease.
Professional Dental Cleanings (also called Prophylaxis)
Professional dental cleanings, also known as prophylaxis, are routine dental procedures that are performed by a dental hygienist or dentist to remove plaque, tartar, and stains from the teeth. This type of cleaning is recommended every six months to maintain optimal oral health and prevent dental problems.
During a dental cleaning, the hygienist or dentist will use specialized tools to remove plaque and tartar from the surface of the teeth, particularly in areas that are difficult to reach with regular brushing and flossing. They will also polish the teeth to remove any surface stains and leave them with a smooth, shiny finish.
Professional dental cleanings are important for maintaining oral health because they help to prevent gum disease, cavities, and bad breath. Gum disease, in particular, can lead to serious health problems if left untreated, including tooth loss and an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
Regular dental cleanings also provide an opportunity for the dentist or hygienist to detect and address any potential problems early on before they become more serious and require more extensive treatment.
Overall, professional dental cleanings are an important part of maintaining good oral health and preventing dental problems. They are a simple, non-invasive procedure that can help keep your teeth and gums healthy for years to come.
Topical Medications
Topical medications can be effective in treating certain forms of gum disease, particularly in the early stages. These medications are applied directly to the gums, where they can help to reduce inflammation, fight infection, and promote healing.
Some of the most common topical medications used in the treatment of gum disease include:
- Antibiotics: These medications can be applied directly to the gums to help kill the bacteria that cause gum disease. Common topical antibiotics used for gum disease include minocycline and doxycycline.
- Anti-inflammatory agents: Medications such as corticosteroids can be applied topically to reduce inflammation and swelling in the gums.
- Chlorhexidine: This antiseptic solution can be applied topically to help kill bacteria and reduce plaque buildup in the mouth.
It’s important to note that while topical medications can be effective in treating gum disease, they are typically used in conjunction with other treatments, such as scaling and root planing or oral antibiotics. It’s also important to follow your dentist’s instructions closely when using these medications to ensure that you get the best possible results.
SURGICAL PROCEDURES
Pocket Reduction Surgery
Pocket reduction surgery, also known as gingivectomy or periodontal flap surgery, is a dental procedure that aims to remove or reduce the depth of periodontal pockets, which are spaces that form between the teeth and gums due to gum disease.
During the procedure, the dentist or periodontist will lift the gum tissue away from the teeth to access the root surfaces and remove any bacteria, tartar, or damaged tissue that is contributing to the pocket formation. The root surfaces may also be smoothed out to help prevent bacteria from adhering to them in the future.
After the cleaning and reshaping of the affected area is complete, the gums are repositioned and sutured back in place. The goal of pocket reduction surgery is to eliminate or reduce the size of the periodontal pockets, making it easier to maintain good oral hygiene and prevent further damage to the teeth and gums.
It’s worth noting that pocket reduction surgery is typically only recommended for patients with moderate to severe gum disease and is often performed alongside other treatments such as scaling and root planing or antibiotics. It’s important to consult with a dental professional to determine the best treatment options for your individual needs.
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is a dental procedure that involves adding bone or bone-like material to the jawbone to promote new bone growth. It can be used to treat a variety of conditions, including gum disease.
In cases where gum disease has caused significant bone loss, bone grafting may be necessary to help rebuild the jawbone and provide a stable foundation for teeth or dental implants. The bone graft material can come from a variety of sources, including the patient’s own bone, synthetic bone, or bone from a donor.
During the procedure, the dentist or periodontist will make a small incision in the gum tissue to access the jawbone. They will then add the bone graft material to the affected area and secure it in place with screws or pins. The patient’s body will then gradually replace the graft material with new bone over several months.
Bone grafting for gum disease can help restore the strength and stability of the jawbone, making it easier to maintain good oral health and prevent further damage to the teeth and gums. It is often performed alongside other treatments, such as pocket reduction surgery or scaling and root planing, to achieve the best possible results.
It’s important to note that not all patients with gum disease will require bone grafting and the best course of treatment will depend on the severity and extent of the disease. A dental professional can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual case.
Guided Tissue Regeneration
Guided tissue regeneration (GTR) is a dental procedure that is commonly used to treat gum disease. It involves using a barrier membrane to guide the growth of new tissue and bone in areas where gum tissue and bone have been lost due to periodontal disease.
During the procedure, the dentist or periodontist will clean the affected area and remove any damaged tissue. They will then place a barrier membrane over the exposed root surface of the tooth, separating it from the gum tissue and allowing new bone and tissue to grow in the space between.
The barrier membrane used in GTR can be made from a variety of materials, including synthetic materials or collagen from animal sources. Over time, the body will gradually absorb the membrane, leaving behind the newly regenerated tissue and bone.
GTR is often used in conjunction with other periodontal treatments, such as scaling and root planing or bone grafting, to help promote the growth of healthy tissue and prevent further damage to the teeth and gums.
Overall, GTR can be an effective treatment option for patients with moderate to severe gum disease who have lost significant amounts of gum tissue and bone. It is important to consult with a dental professional to determine if GTR is the right treatment option for your individual needs.
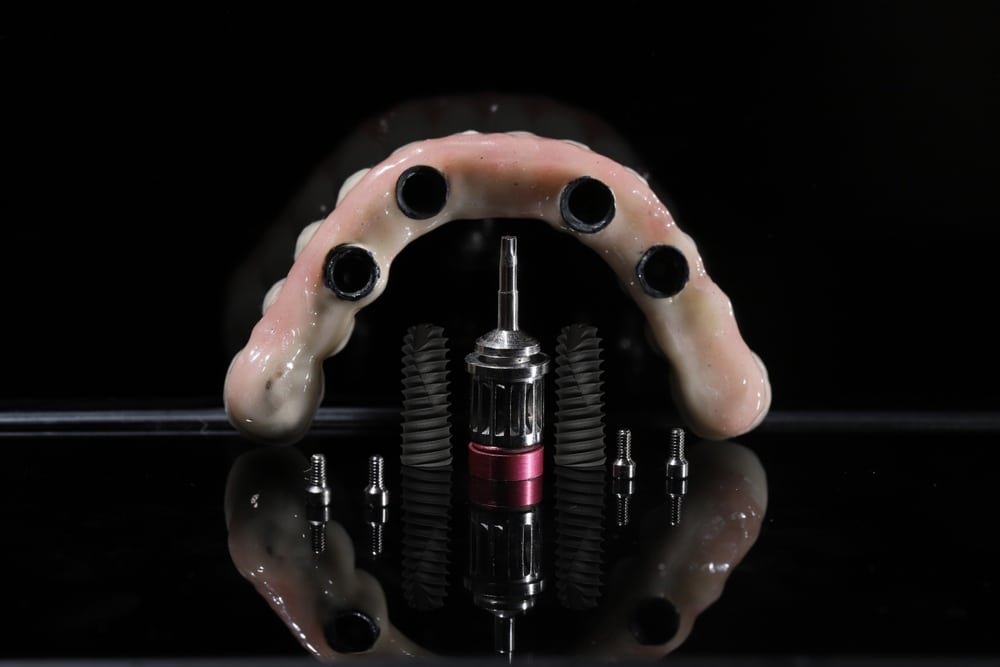
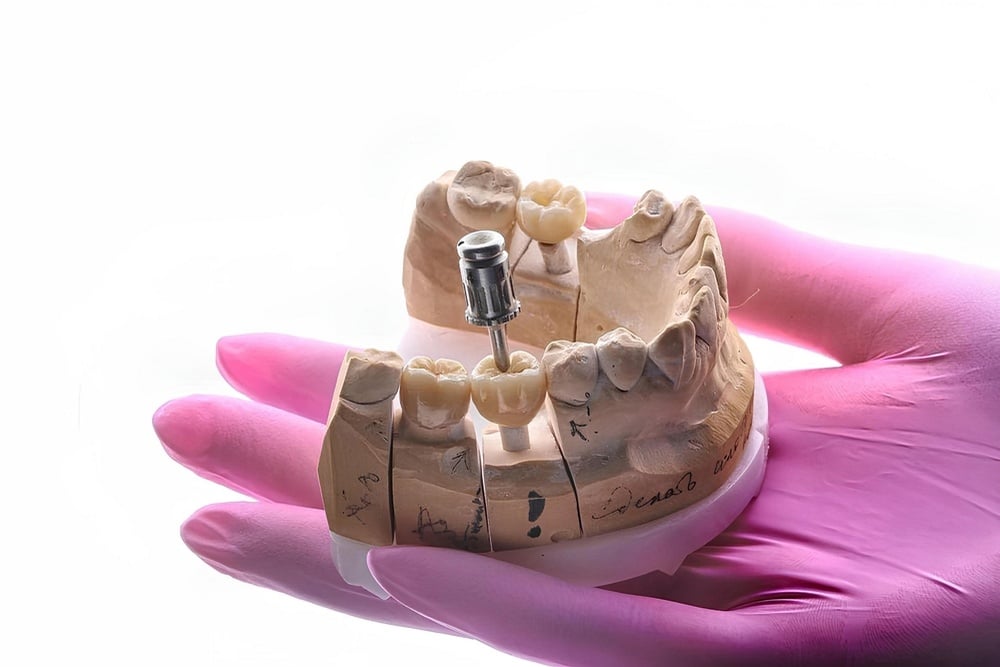
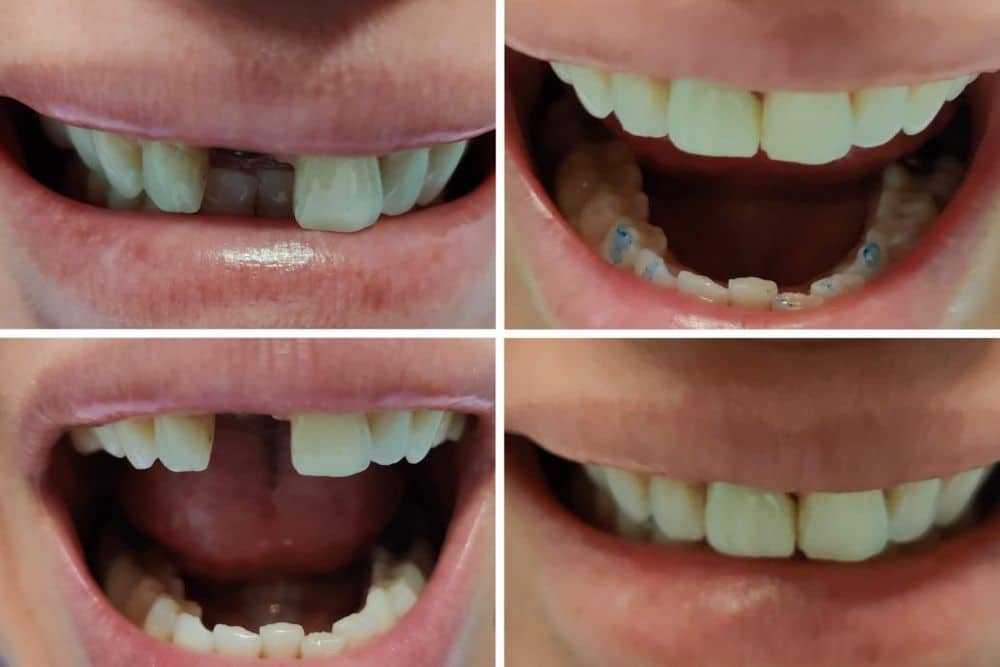
Dental Implants
Dental implants are a popular treatment option for patients who have lost one or more teeth due to gum disease. They are surgically placed into the jawbone to provide a permanent, stable foundation for replacement teeth.
Before dental implants can be placed, it is important to treat any underlying gum disease to ensure the success of the implant procedure. This may involve treatments such as scaling and root planing, pocket reduction surgery, or bone grafting.
Once the gum disease has been treated and the jawbone is healthy enough to support the implant, the dentist or oral surgeon will place a titanium post into the jawbone. Over time, the post will fuse with the surrounding bone, creating a strong and durable foundation for the replacement tooth.
After the post has integrated with the bone, an abutment is attached to the post, and a custom-made dental crown is attached to the abutment. The crown is designed to look and function like a natural tooth, allowing patients to eat, speak, and smile with confidence.
Dental implants can be a great option for patients with gum disease who have lost one or more teeth, as they provide a permanent, long-lasting solution that is designed to look and function like natural teeth. However, it’s important to note that not all patients may be candidates for dental implants, and a dental professional can help determine the best course of treatment for each individual case.
The most effective treatment for periodontal disease will depend on the severity and extent of the disease in each individual case. In general, treatment for periodontal disease is aimed at controlling the infection, reducing inflammation, and preventing further damage to the gums and teeth. It’s important to note that proper oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, is also crucial for preventing and treating periodontal disease. A dental professional can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan for each individual case based on the severity and extent of the disease. Do you need a dental check-up? Dental Arts San Diego is here to help! Schedule an appointment by calling (619) 444-1001 or clicking here. We are located at 707 Arnele Avenue, El Cajon, CA, 92020.